About this course
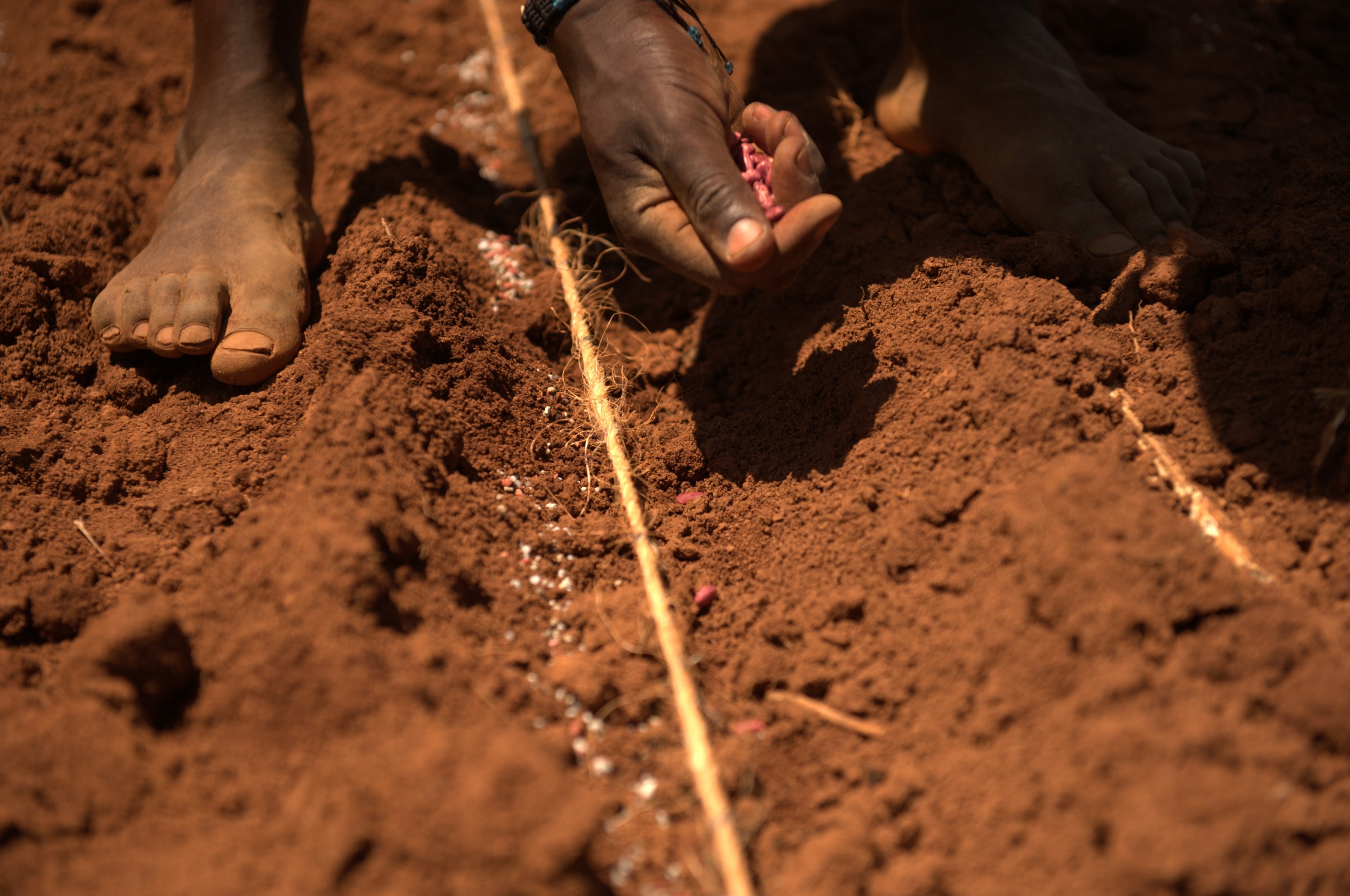
This course provides an overview of the different fertilizer placement methods and management strategies that farmers can use to improve the effectiveness of fertilizer application. The course covers critical considerations for fertilizer placement, including the source, rate, and time of nutrient application, the location of plant roots, and the mobility of nutrients in the soil. Students will learn about different placement methods, including broadcasting, banding, spot application, and deep placement, and will gain an understanding of when each technique is most appropriate. The course also covers strategies for managing spatial variability in soil fertility within and between fields and considerations for tillage systems and conservation practices.
Comments (0)
By considering soil type, plant needs, fertilizer type, environmental factors, and equipment, growers can make informed decisions that lead to optimal plant growth and yields. These considerations are also essential for sustainable agricultural practices and best farming practices that consider climate change. Proper fertilizer placement is a critical component of climate-smart agriculture.
Farmers must carefully consider different placement methods to optimize fertilizer applications, reduce nutrient loss, and ensure that crops receive the necessary nutrients for growth and development. By adopting sustainable agriculture practices, such as effective fertilizer management, farmers can improve crop yields and quality and contribute to climate change mitigation.
Spatial variability refers to the differences in soil properties within a field. Factors like soil type, slope, drainage, and previous land use can cause spatial variability. Understanding spatial variability is crucial in developing efficient and effective fertilizer placement methods and management strategies.
This module explores different tillage systems and conservation practices that can enhance soil health and productivity, essential for climate-smart agriculture. Climate change causes significant challenges for agriculture, but smart agriculture practices such as conservation tillage, cover cropping, crop rotation, and mulching can help mitigate its impact
Quiz & Certificates
.jpg)




